 With the growth of hybrid and electric vehicles over recent years, one question that often comes up is, “what happens to all of those old EV and Hybrid batteries when they get replaced; where do they go?” Well, the answer to that question still seems to be developing. Of course, there are traditional recycling means in place to capture the various materials that make up these batteries, but what if the batteries life could be extended, still serving a purpose, before reaching the standard recycling process? Is there a greener / cleaner way to extend these batteries life? Yes, there is!
With the growth of hybrid and electric vehicles over recent years, one question that often comes up is, “what happens to all of those old EV and Hybrid batteries when they get replaced; where do they go?” Well, the answer to that question still seems to be developing. Of course, there are traditional recycling means in place to capture the various materials that make up these batteries, but what if the batteries life could be extended, still serving a purpose, before reaching the standard recycling process? Is there a greener / cleaner way to extend these batteries life? Yes, there is!
A misconception or a point that is often overlooked when it comes to EV and Hybrid batteries and their “life cycle” in vehicles, is that, even after they are no longer suitable for their original purpose, they may still be used for other purposes, providing adequate power, that can extend or give them a 2nd life, by being used as energy storage units. Battery energy storage capacity diminishes over time, to a point where battery packs are no longer suitable for use in vehicles, but they can still be useful in other ways such as energy storage units.
One example of a second life battery project is a partnership between Toyota and Indy Power Systems, on the Lamar Buffalo Ranch in Yellowstone National Park, one of the greenest parks in the world. This project uses 208 customer Camry hybrid battery packs from Toyota dealerships that have been replaced by new batteries when their original battery reached its end of life cycle. The hybrid batteries provide 85kWh of energy storage created by the ranch’s solar panels to ensure continuous power as the system charges and discharges.
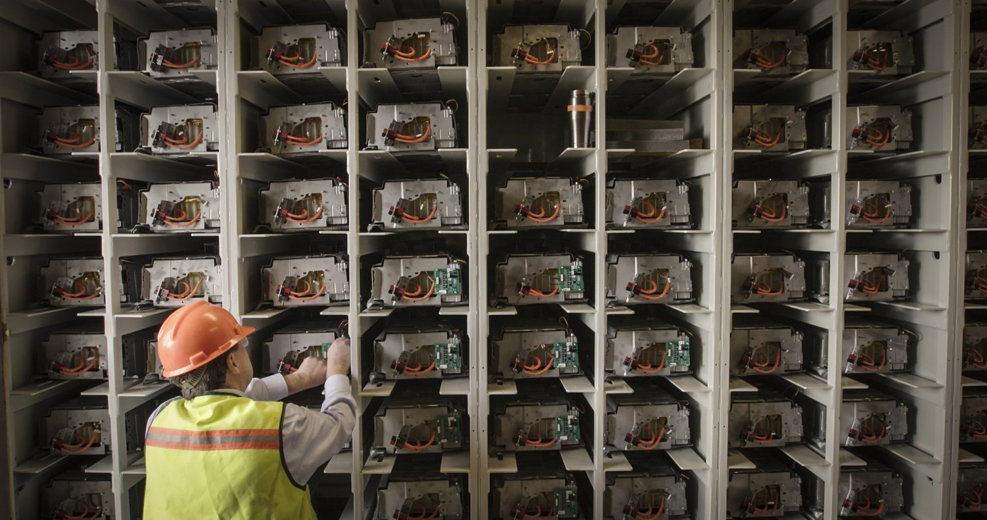

Toyota’s hybrid battery repurposing project at Lamar Ranch in Yellowstone National Park, using 208 used Camry hybrid batteries, that have been decommissioned from vehicle use. Batteries are paired with wind mills which power the ranch.
A similar project using EV batteries has been spearheaded by BMW on the grounds of their Leipzig plant in Germany. BMW has been able to use 500 new and used BMW i3 EV batteries working together with wind power, to power the Leipzig plant. Some new i3 batteries were used along with used ones, as there are a limited amount of used i3 batteries available with the i3 car only being a few years old, with most vehicles still having healthy, functioning batteries.
 There is a further scalable capacity up to 200 more batteries (700 total) at the plant. The capacity of 700 high voltage batteries is the equivalent of an electric range of 100,000km in a BMW i3. The stationary storage battery farm is also integrated with public power grid, which enables its electricity to be marketed.
There is a further scalable capacity up to 200 more batteries (700 total) at the plant. The capacity of 700 high voltage batteries is the equivalent of an electric range of 100,000km in a BMW i3. The stationary storage battery farm is also integrated with public power grid, which enables its electricity to be marketed.
The market for using older, condemned EV and hybrid batteries is one that is currently conducting a lot of research and seems to be continually growing, either as off the grid projects, or supplementing existing warehouses/businesses that use the grid to elevate grid demand and costs. This should continue to be a growing market in the years to come as more and more automotive EV and hybrid batteries are replaced.
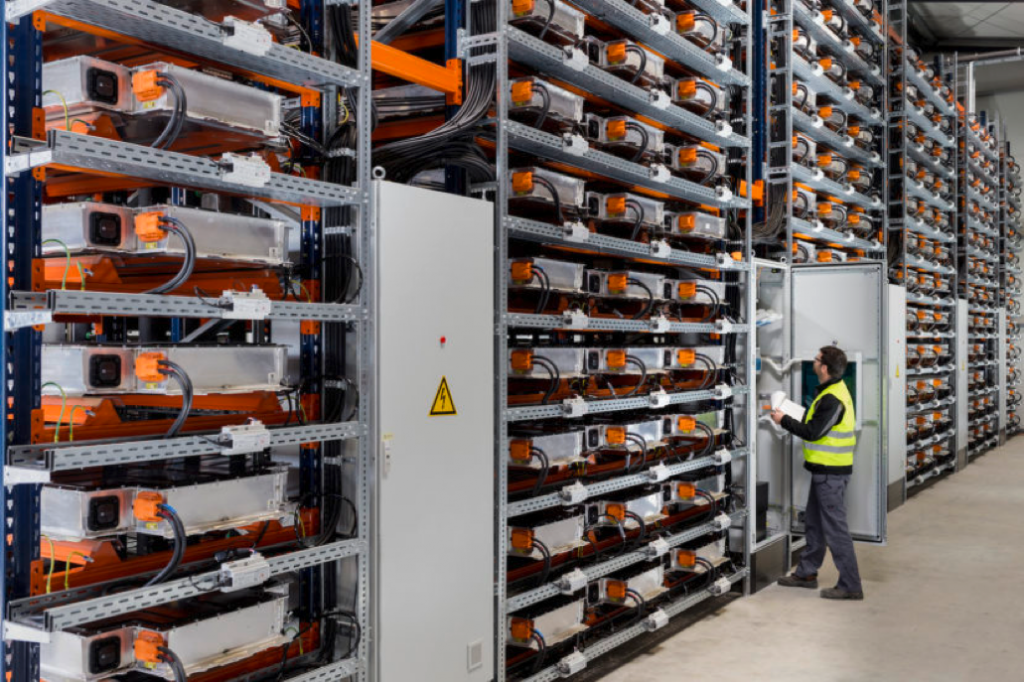

BMW’s Leipzig production plant uses 500 new & used i3 EV batteries paired with wind mills to help power the factory.


Leave a Reply
Your email is safe with us.